Palm oil and palm kernel oil extraction process
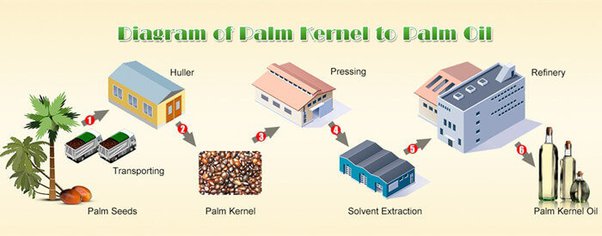
1.Weighing
Transport palm fruit to factory after truck weighing so as to make prompt settlement and production cost subsequent.
2.Unloading fruit
Fresh Fruit Bunches (FFB) are sent to fermentation tank through transportation machinery after sieving and impurities removing. The time from picking up to fermentation should be less than 24 hours, or the free fatty acid(FFA) will rise, which will not be conductive for further processing and production of palm oil from palm oil making machine.
3.Digestion of the fruit
Digestion is the process of releasing the palm oil in the fruit through the rupture or breaking down of the oil-bearing cells. The digester commonly used consists of a steam-heated cylindrical vessel fitted with a central rotating shaft carrying a number of beater (stirring) arms. Through the action of the rotating beater arms the fruit is pounded. Pounding, or digesting the fruit at high temperature, helps to reduce the viscosity of the oil, destroys the fruits’ outer covering (exocarp), and completes the disruption of the oil cells already begun in the sterilization phase. Unfortunately, for reasons related to cost and maintenance, most small-scale digesters do not have the heat insulation and steam injections that help to maintain their contents at elevated temperatures during this operation.
Contamination from iron is greatest during digestion when the highest rate of metal wear is encountered in the milling process. Iron contamination increases the risk of oil oxidation and the onset of oil rancidity.
4.Threshing(removal of fruit from the bunches)
The fresh fruit bunch consists of fruit embedded in spikelets growing on a main stem. Manual threshing is achieved by cutting the fruit-laden spikelets from the bunch stem with an axe or machete and then separating the fruit from the spikelets by hand. Children and the elderly in the village earn income as casual labourers performing this activity at the factory site.
Threshing machine will separate both palm fruits and empty fruit bunches(EFB) after FFB soften duirng fermentation. Empty fruit bunches (EFB). EFB are sent to send to garden as fertilizer, fuel or other purposes after conveying and hoarding.
5.Pressing (Extracting the palm oil)
Palm fruit by stirring and squeeze broken by mashed tank, and then put into the screw press machine to press oil. Then, containing sand, water, and oil liquid part put into the purifier separation to get crude palm oil. The press cake (including fiber and nuclear) into the next process.

6.Clarification and drying of oil
The main point of clarification is to separate the oil from its entrained impurities. The fluid coming out of the press is a mixture of palm oil, water, cell debris, fibrous material and ‘non-oily solids’. Because of the non-oily solids the mixture is very thick (viscous). Hot water is therefore added to the press output mixture to thin it. The dilution (addition of water) provides a barrier causing the heavy solids to fall to the bottom of the container while the lighter oil droplets flow through the watery mixture to the top when heat is applied to break the emulsion (oil suspended in water with the aid of gums and resins). Water is added in a ratio of 3:1.
The diluted mixture is passed through a screen to remove coarse fibre. The screened mixture is boiled from one or two hours and then allowed to settle by gravity in the large tank so that the palm oil, being lighter than water, will separate and rise to the top. The clear oil is decanted into a reception tank. This clarified oil still contains traces of water and dirt. To prevent increasing FFA through autocatalytic hydrolysis of the oil, the moisture content of the oil must be reduced to 0.15 to 0.25 percent. Re-heating the decanted oil in a cooking pot and carefully skimming off the dried oil from any engrained dirt removes any residual moisture. Continuous clarifiers consist of three compartments to treat the crude mixture, dry decanted oil and hold finished oil in an outer shell as a heat exchanger.

7. Fiber separation
The extruded cake-like fibers are broken into the wind selection system to separate the fibers from the core.
8.Nucleolar separation
The nucleolar is divided into kernel and shell by nuclear crusher after separated with fiber. Then, after washing and winnowing separation system separate the nuclear and shell. The shell is stored as fuel for entering the boiler fuel system. The kernel is stored after drying.
9.Palm kernel press oil
Palm kernel oil extraction process, including crushing, rolling billet, steaming and pressing. Its production process and equipment similar to the general oil.
10.Steam boilers
The fibers and core shells are transported to the boiler for use as fuel. Steam boilers are mainly used to provide steam for power generation, fermentation and heating, the steam boiler fuel used in the manufacture of palm oil is separated from the fiber and shell.
11.Sewage treatment
Used the sewage of the pipeline, the process wastewater through the sewage treatment facilities, discharge standards.
palm oil processing machine main features:
1, our company adopts hydraulic segmented discharge in palm fruit unloading, cleaning, storage platform;
2, palm fruit oil press machine adopts double helix hydraulic continuous discharging, greatly improving the production efficiency;
3, the use of diesel generator and steam turbine generator is more environmental protection and energy saving, electricity power for production and life;
4, our water treatment system, through sedimentation, filtration, dosing process, ensure the quality of the water, also ensure the quality of palm oil;
5, adopting the remote substation technology, more energy efficient, improve the production efficiency.
Palm Oil
Palm oil is a tropical woody plant oil, it is the world’s second largest vegetable oil varieties in the production, consumption and international trade volume, only ranking after soybean oil, known as “the world’s three largest oil plant” with soybean oil, rapeseed oil, has more than five thousand years of food history Resources and Information. present, Malaysia and Indonesia is two largest palm oil producing countries in the world. Besides, there are many palm oil mills in Africa, such as Nigeria, Ethiopia, Congo, Ivory Coast, etc.
The best alternative to unsustainable palm oil is sustainable palm oil. Not all oil plantations are newly established on the charcoal of orangutan habitat. Some are managed in line with best practice and provide a valuable source of income for an otherwise poor community.
Palm trees propagate by producing nuts. Aquanuts in fact, they can float on the ocean waters to a new island, or down the sultry Nile.
A few coconuts per tree, or thousands of little seeds on some ornamental palms. Somewhere in the middle is a species or two that produce a vegetable oil when the nuts are pressed.

Indonesia [and the Philippines] are destroying their natural rainforest to make a quick buck. Every year thousands of hectares of biodiverse land are burnt, the animals destroyed, and monoculture palm farms are planted so Americans and the EU can have cheap cookies with our coffee latees.
